Exploration and Prospecting
Jordan Phosphate Mines Company carries out exploration/ prospecting operations in search of phosphate ores being a core business of the Company and a significant component of its growth. The Company seeks to enhance the geological reserve of phosphate ores in order to safeguard, develop, and diversify its operations. The Company relies on the latest computerized technologies and up-to-date mechanisms to explore phosphate ores and assess them to identify the quantities of phosphate ores and their grades. In compliance with the valid laws and bylaws, the Company applies to the Energy and Minerals Regulatory Commission to obtain a license of prospecting phosphate ores.
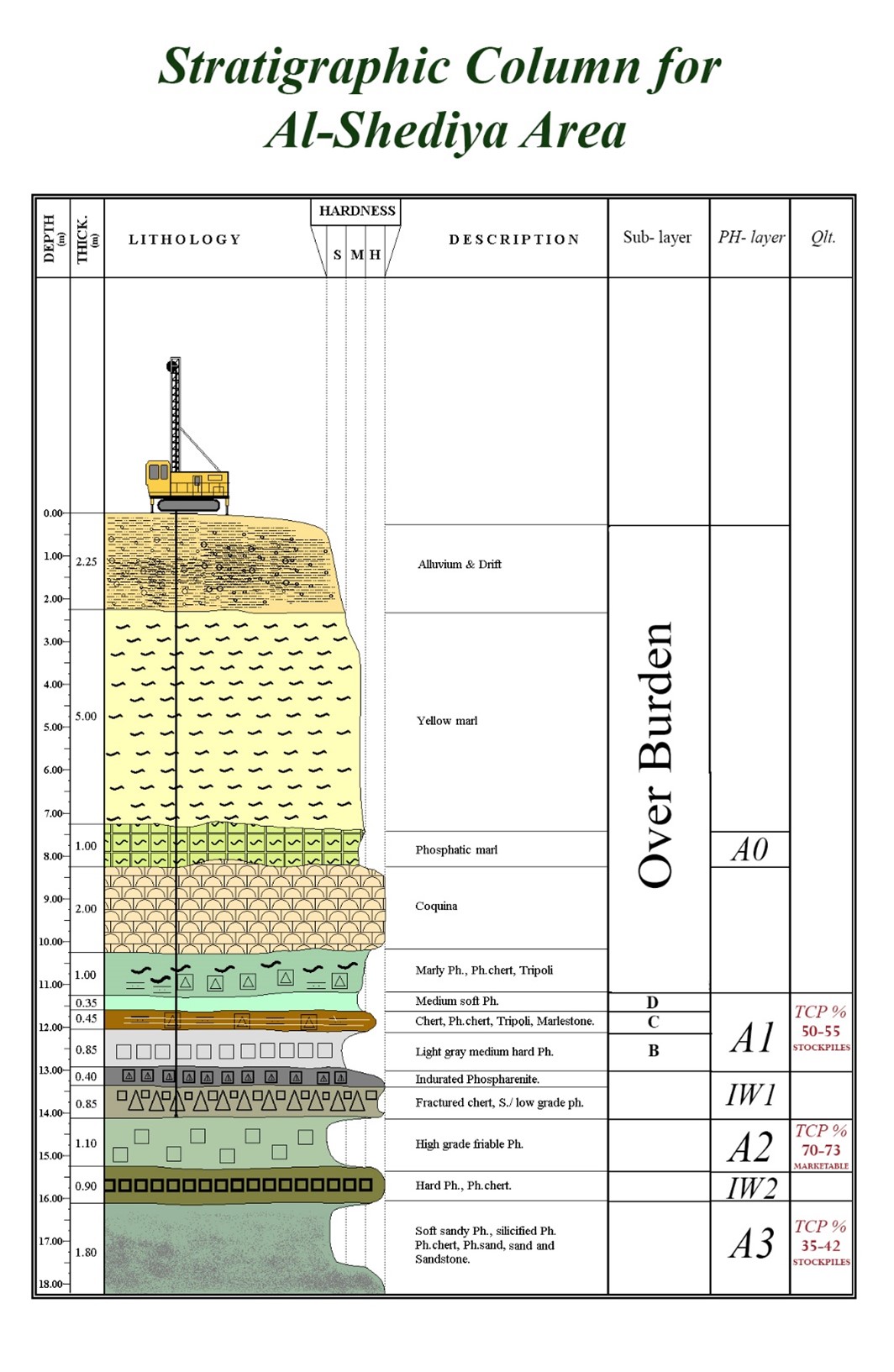
The exploration and prospecting operations are implemented along several phases starting with a study of the geological maps of targeted areas so that the prospective areas with potentials of available phosphate ores therein can be identified. Afterwards, field surveys are then conducted for the purpose of exploration and search for places that reveal phosphate or stratigraphic tracking of the geological column. Based on these procedures, a plan for drilling exploratory wells is devised to identify a network of wells starting from a distance between them up to (800 m * 800 m). Accordingly, and based on the results exploration operations continue until a distance of up to (100 m * 100 m) is reached to have access to the proved geological reserve. The latest computerized programs and technologies are used in computing the quantities and qualities in addition to drawing geological and typographical maps of phosphate ores. As at 1.10.2024, the geological reserve (proven, possible and potential) was as follows: (per million cubic meter)
Mine | Proven | Possible | Potential | Total |
AlWadi AlAbyad | 3,975 | - | 10,000 | 13,975 |
AlHasa | 8,383 | 10,000 | - | 18,383 |
Eshidia | 234,874 | - | 50,000 | 284,874 |
TOTAL | 247,232 | 10,000 | 60,000 | 317,232 |
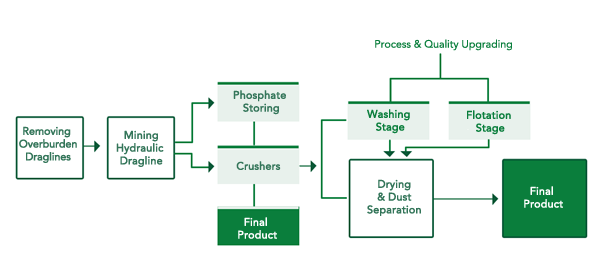
Perations and Phases of Mining, Manufacturing, and Transporting Rock Phosphate
First: Phosphate Mining Operations
Since its inception to the present date, Jordan Phosphate Mines Company has embraced two methods of mining works as follows:
a.Underground Mining:
This method had been used early when the Company started its work prior to the seventies of past century in order to mine the ores in Rusaifa and AlHasa. However, this method was stopped in 1959 as it is an intensive labor method and is of poor levels of public safety.
b.Open Cast Mining
Jordan Phosphate Mines Company had first used this method of mining after 1959 to mine phosphate ores in AlHasa although it had relied on Rusaifa Mine only. The open cast mining is implemented in several phases as follows:
(i) Removal of Overburden:
This overburden (soil cover) is removed via drilling and blasting the layers in order to remove them using the electric and/or hydraulic draglines. The number of wells and quantities of explosives used are identified according to the nature of the upper overburden layers and their solidity.
(ii) Mining and Compilation Operations of Phosphate Layers:
Via the operations of upper overburden removal, the surface of phosphate layers can be accessed. The phosphate mining operations start with the quality control process as representative samples are taken for the phosphate layer and the chemical and physical analysis is conducted on the rock phosphate. This analysis results set the subsequent steps in dealing with phosphate. Accordingly, the operations of phosphate mining are implemented using the traditional machinery as relevant to the nature of phosphate which is loaded and transported to go through the next phase according to the physical and chemical analyses.
(iii) Phosphate Screening and Crushing:
The chemical and physical analyses processes are done for the phosphate. Based on these analyses, the subsequent phase is identified. Screening is done only if the phosphate is soft; if it is solid, the phosphate undergoes screening and crushing operations in order to remove the impurities of phosphate and obtain the required size.
(iv) Phosphate Processing Phase and Floating Unit:
After implementing the screening and crushing processes and obtaining the relevant size, representative samples are collected to to quality control and conduct chemical analyses of this product. Based on the results, the phosphate that does not require manufacturing or processing later on will be ready for marketing or for use in manufacturing industries. If the analyses reveal low grade phosphate that contains impurities such as iron oxides, aluminum oxides, silica, and clay minerals, it is sent to the floating units (beneficiation plant) where the impurities are removed and the P2O5 concentration is increased through one or two phase(s). Some phosphate grades require one processing phase whilst others need two phases of processing. The main processing phases are:
i) The Phosphate Washing Plant:
The process starts with the homogenization of the raw phosphate with rotating cyclones at certain speeds, and a specific percentage of water is added to these cyclones and homogenized. This method takes place along several phases. To get rid of the clay materials associated with phosphate and increase the concentration of (P2O5).
ii) Floatation Plant:
Based on the above chemical analyses of phosphate and identifying the elements and impurities in the phosphate, the impurities are removed via the first phase (phosphate washing). The main impurities include silica; this phase is implemented by adding chemicals to the raw phosphate and floating of the impurities to be removed.
Jordan Phosphate Mines Company owns two units for phosphate processing. One is located in AlWadi AlAbyad Mine with a production capacity of 500-700) thousand tons per year and another unit in Eshidia Mine the production capacity of which amounts to (1-1.3) million tons per year. To realize sustainability and exploitation of all grades of phosphate, increase the production capacity, and increase the market share of the Company, the Company seeks to implement major projects including the construction of a processing unit to increase the phosphate concentration in Eshidia Mine with a production capacity of (2) million tons/year with high ration grades and specifications. Production is expected to start in this unit during the first quarter of 2025. Another project is to construct the unit of raising and processing the phosphate ores in AlHasa Mine with a production capacity of (0.5) million tons/year.
v) The Phosphate Drying Phase:
Among the analyses conducted on phosphate is the moisture degree as it is important in the manufacturing processes of phosphate. Due to the use of water in the previous phase (the beneficiation of phosphate), the water increases in phosphate to a high level. As such, this water must be removed via the phosphate drying unit (dryers); these are rotating cyclones including a burning unit at high temperatures and air is pressed therein; phosphate is pumped inside these rotating dryers provided with hot air to dry the phosphate and get rid from high moisture to be of an acceptable percentage for both the phosphate manufacturing processes later on and to fulfill the requirements of customers purchasing the raw phosphate.
The Company owns units (dryers) in all of its mines. The Company applies the competitiveness policies in announcing tenders for phosphate mining. As such, the terms of reference require the contractor to construct his own dryer units in order to keep the moisture degree at 3% maximum.
Second: The Phase of Phosphate Transport:
After implementing all of the above phases, physical and chemical analyses are conducted on the produced phosphate. According to the results, the entity to which the phosphate will be transported is identified as follows:
Associate and subsidiary companies of JPMC in Eshidia Mine to be used in producing phosphoric acid.
The Industrial Complex in Aqaba affiliated to JPMC to be used in phosphate acid and phosphate fertilizers production.
The Raw Phosphate Exportation Port in Aqaba; it is a specialized port and owned by JPMC. The phosphate vessels are loaded there to be transported to customers worldwide.
Plan no. (1) llustrates the phases of mining and manufacturing the phosphate:-